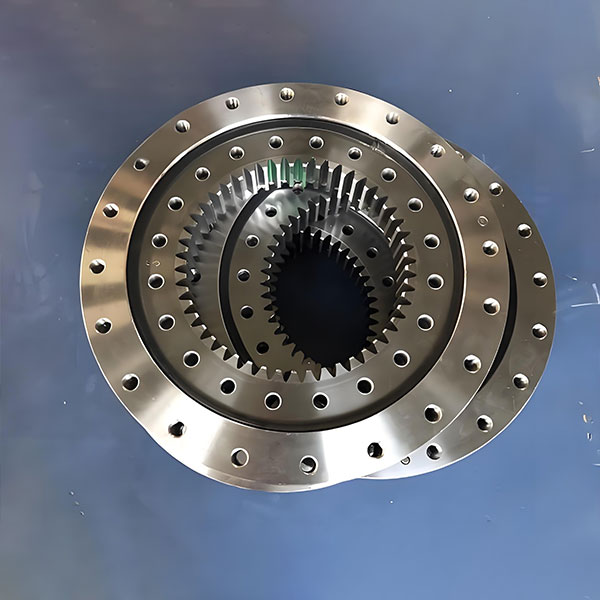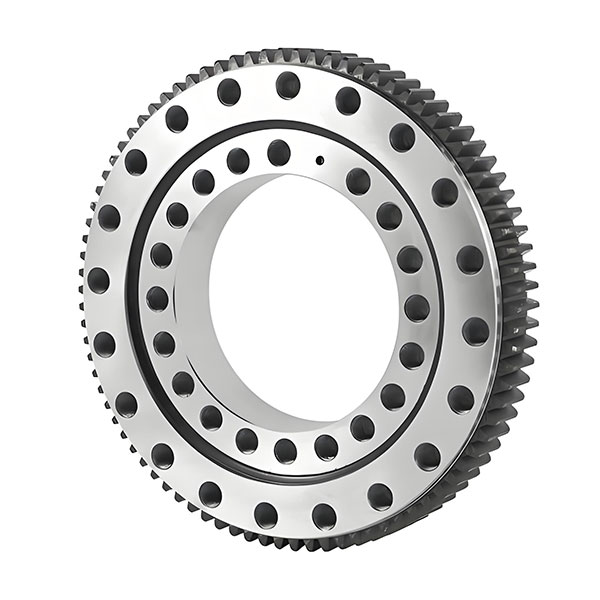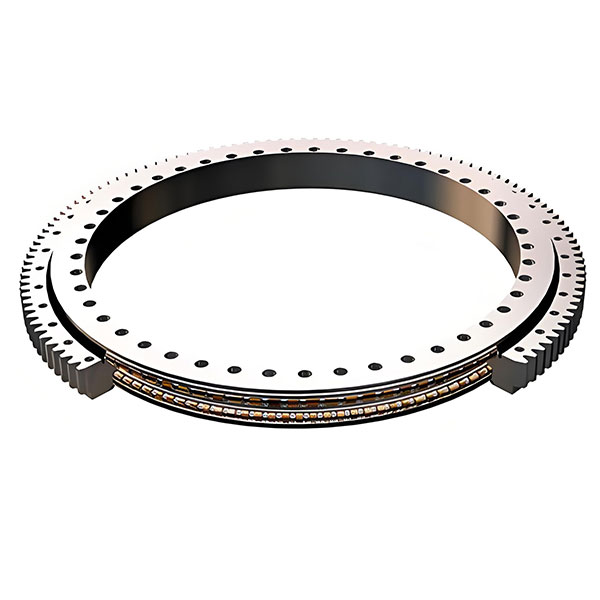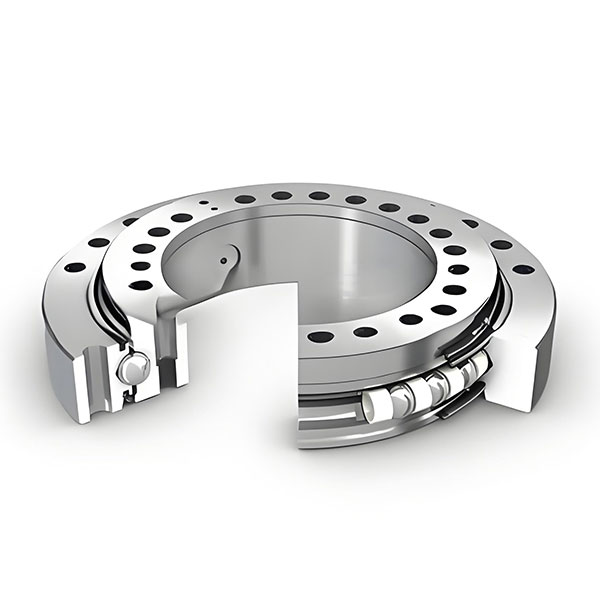
Gear rod
Gear rod
Tough wheels are indispensable elements in many mechanisms that surround us every day. Imagine a bicycle - toothed wheels, rotating relative to each other, set in motion a chain and a wheel, making us mobile. Or a clock where the smooth movement of the shooter depends on the exact interaction of the cloves. These simple, but important details, hidden from our gaze, do difficult work.
Types of gear wheels and their purpose
There are many types of gear wheels adapted to different tasks. Some have direct teeth, allowing transmitting rotation almost without losing energy. Others, with complex profiles of teeth, provide a more smooth, or vice versa, sharper rotation. Some wheels are used to increase or decrease the rotation speed, as in the mechanisms of lifting cargo, where a lot of torque is needed, but not high speed. Others - for accurate transmission of rotation, as in clock mechanisms where the most important is accuracy.
How gear wheels work
The work of the gear wheels is based on the principle of interaction of teeth. The teeth of one wheel are precisely clinging into the teeth of another. Imagine how the links of the chain on a bicycle are hooked by the teeth: each rotation of one wheel provokes the rotation of the other. An important point is the compliance of the shape of the teeth. If the forms are not suitable for each other, the wheels will not be able to work correctly and significant problems will arise. Incorrect interaction can lead to a breakdown and damage to the mechanism.
Meaning in modern technology
Goard wheels play a huge role in modern technology. From complex industrial machines to household appliances, the transmission of rotation with gear wheels provides the operation of many mechanisms. Their use permeates all spheres of our lives, from cars and aircraft to computers and phones. They are the basis for effective and reliable energy transfer. Progress in the design and production of gear wheels allows you to create more and more complex and accurate mechanisms that contribute to the development of technology.
AppropriateProducts
Corresponding products
The best soldproducts
The best -selling productsConnectedsearch
Related search- Cheap construction equipment turning ring of the country's main buyers
- Price for replacing oem gears
- Cheap granulator mill of the supports and high bearings prices
- Cheap suppliers Excavator rotary bearing repair or recovery
- The main countries of the OEM of the rotary bearings
- 1-speed program suppliers from China
- Suppliers of OEM GOST turning bearings
- Prices for front bearings in China
- Suppliers of OMA supporting bearings
- Bearing suppliers 3 in China